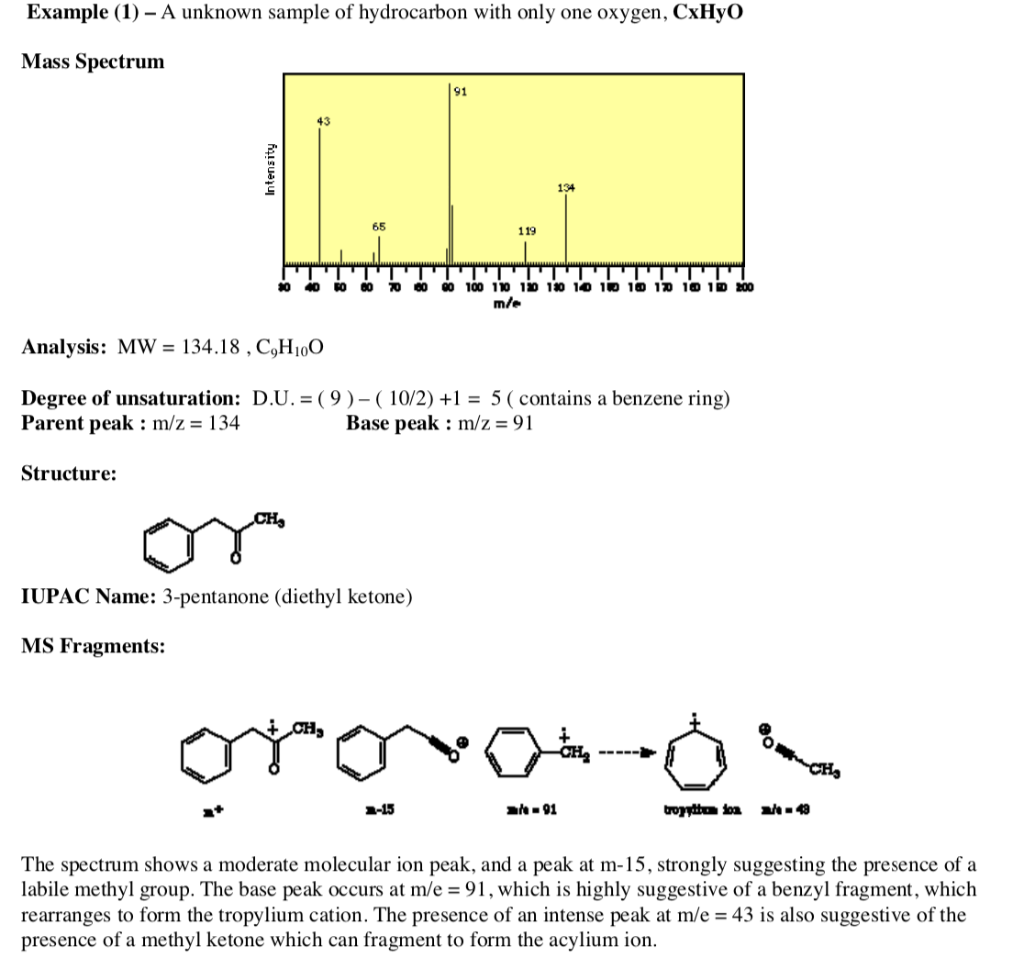
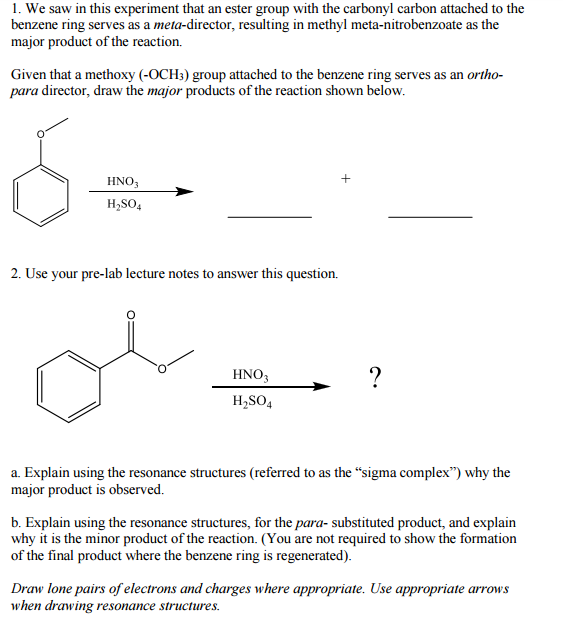
Benzene Ring With Ketone Attached
If you draw a benzene ring with one group attached you have drawn a phenyl group.
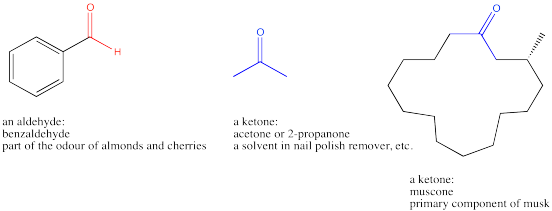
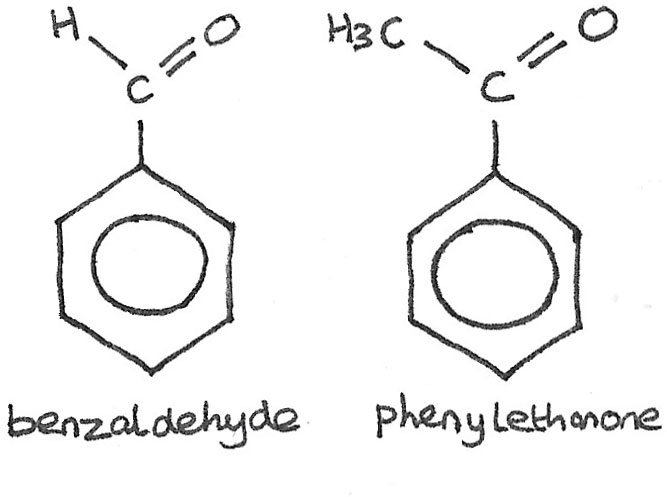
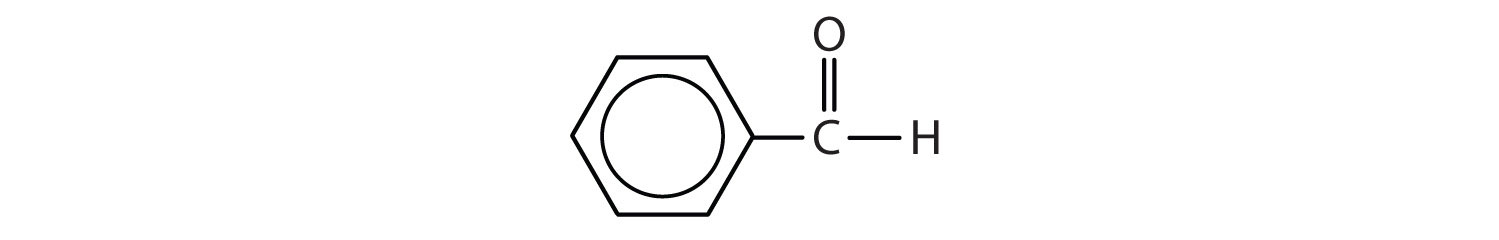
Benzene ring with ketone attached. Since there is only one substituent on the benzene ring we do not have to indicate its position on the benzene ring as it can freely rotate around and you would end up getting the same compound figure 8. Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula c 6 h 6 the benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Remember that the phenyl group is a benzene ring minus a hydrogen atom c 6 h 5. Because of the full or partial positive charge on the element directly attached to the ring for each of these groups they all have a moderate to strong electron withdrawing inductive effect known as the i effect.
The name is self obvious. 1 2 or 1 3 or 1 4 dichlorobenzene c 6 h 4 cl 2. Whenever you draw a benzene ring with one other thing attached to it you are in fact drawing a phenyl group. Chlorobenzene c 6 h 5 cl and.
For example h 2 c o is methanal more commonly called formaldehyde since an aldehyde carbonyl group must always lie at the end of a carbon chain it is always is given the 1 location position in numbering and it is not necessary to include it in the name. Halo arenes aryl a romatic halides. As it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Phenylethanone can also be reduced to produce ethylbenzene.
The iupac system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix al to aldehydes. Most importantly we have the first part of the final product of the reaction which is a ketone. Phenylamine is a primary amine and contains the nh 2 group attached to a benzene ring. You could therefore although you never do call it phenyl chloride.
The old name for phenylamine is aniline and you could also reasonably call it. This is a simple example of a halogen attached to the benzene ring. C 7 h 7 cl chloromethylbenzene or chloromethyl benzene benzyl chloride. The oxygen atom in ketones is directly attached to a hydrogen atom.
It is not a true aryl halogen compound the halogen atom is in a non aromatic side chain so it. Ketones contain an oxygen atom. This is known as the clemmensen reduction and involves heating the ketone with amalgamated zinc a mixture of zinc and mercury and concentrated hydrochloric acid for a long time. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals.
Or aryl halide aromatic halogen compounds the halogen is directly attached to the benzene ring. During the third step alcl 4 returns to remove a proton from the benzene ring which enables the ring to return to aromaticity. Select the correct choice below. Ketones have higher boiling points than the corresponding alkanes.
This indirect route is the best way of getting an alkyl group attached to a benzene ring. In doing so the original alcl 3 is regenerated for use again along with hcl. For example chlorine cl attached to a phenyl group would be named chlorobenzene chloro benzene.